Learn about concussion symptoms and how to start feeling better.
All concussions are serious. If you hit your head or body hard, see a health care provider right away.
Quick facts:
- A concussion is a brain injury that can happen from a hit on the head or body.
- Concussions are also called “mild traumatic brain injuries”. They are usually not life-threatening and often do not cause lasting problems.
- Concussions are common after car accidents, falls, sports, or assaults.
- You don’t have to “blackout” (lose consciousness) to have a concussion.
- After a concussion, you may feel confused, dizzy, or have trouble remembering what happened.
- Most people recover fully within two to four weeks. Older adults and those with past concussions may take longer.
- Knowing about your concussion and following your health care provider’s advice can help you recover better.
Warning signs - when to get help
Right after an event that could cause a concussion, both of these things should happen:
- You should be removed from the activity.
- A doctor or nurse practitioner should check you. This can be done at an emergency department, clinic, or doctor’s office.
If any of these “red flags” appear within the first few days, go to the nearest emergency department or call 9-1-1:
- Neck pain or tenderness
- Double vision
- Weakness, tingling, or burning in the arms or legs
- Severe headache or a headache that gets worse
- Seizure or convulsion
- Blacking out (lose consciousness)
- Getting drowsy
- Vomiting
- Not able to recognize people or places
- Getting restless, agitated, or hostile
Watch Dr. Newhouses’s video to learn more.
The Concussion Awareness Training Tool (CATT) can also guide you on what to do after a concussion.
- Concussion: Minor head injury in children
- Concussion: Minor head injury in adults
- Concussion: A guide to understanding your recovery
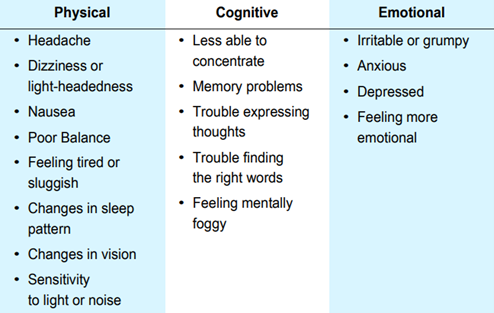
Common signs of a concussion
After a concussion, you might notice different signs or effects. Everyone is unique, so your signs may differ from others.
These signs can be uncomfortable, but they usually improve over time. They rarely cause serious health issues. Most of the time, they heal on their own without special treatment.
Even if your injury seems minor, it's important to know the signs of a concussion.
Additional resources
For adults (18 years and older):
For children and teens (under 18 years):
